LCD Interface Selection for Industrial Panel PCs and Monitors

Engineering Considerations Beyond Basic Signal Compatibility In industrial Panel PC and monitor projects, LCD interface selection …

As industrial display systems continue to evolve, interface selection has become more complex than simply choosing a compatible connector.
With HDMI, DisplayPort (DP), and USB-C all appearing in industrial specifications, engineers and system designers often ask the same question:
Which interface is best for industrial applications?
The reality is that each interface was developed with different design priorities.
Understanding how these technologies behave in industrial environments is essential for making a practical and reliable choice.
Unlike consumer electronics, industrial displays are often deployed in systems that require:
The display interface directly affects system reliability, integration effort, and maintenance complexity.
For this reason, interface selection should consider more than bandwidth or resolution support.
HDMI is one of the most commonly used display interfaces and is widely supported by industrial PCs, embedded controllers, and media players.
HDMI has evolved through multiple versions, and behavior can vary between chipsets and implementations.
In industrial systems, this may lead to differences in EDID handling or signal negotiation between batches of hardware.
HDMI is often used successfully in cost-sensitive or moderately demanding industrial applications, especially where replacement flexibility is important.
DisplayPort was developed with higher bandwidth and system-level integration in mind.
DisplayPort cables and connectors are generally more sensitive to routing and length compared to HDMI.
However, in fixed industrial installations where cabling is well-controlled, DP offers a high level of stability.
DP is commonly selected for industrial HMIs, control rooms, and fixed automation systems where consistent signal performance is required.
USB-C is increasingly visible in modern hardware due to its compact form factor and versatility.
USB-C is not a single display standard.
Display functionality depends on protocol support, controller implementation, and system configuration.
In industrial environments, this flexibility can introduce:
USB-C is best suited for controlled systems where interface behavior is fully validated, rather than open or long-lifecycle industrial deployments.
| Aspect | HDMI | DisplayPort | USB-C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Availability | Very high | Moderate | Increasing |
| Integration complexity | Low | Medium | High |
| Long-term consistency | Medium | High | Variable |
| Cable sensitivity | Low | Medium | High |
| Industrial predictability | Medium | High | Project-dependent |
Rather than asking which interface is “best,” it is often more useful to ask which interface introduces the least uncertainty for a given system.
In practice:
The optimal choice depends on system architecture, lifecycle expectations, and integration constraints.
Industrial display interfaces are not interchangeable commodities.
Each technology brings its own assumptions, benefits, and trade-offs.
By understanding how HDMI, DisplayPort, and USB-C behave in real industrial environments, system designers can make more informed decisions and reduce integration risk over the lifetime of a project.

Engineering Considerations Beyond Basic Signal Compatibility In industrial Panel PC and monitor projects, LCD interface selection …

Why Higher Ingress Protection Does Not Always Mean Higher Reliability In industrial Panel PC projects, IP …

1. Understanding Capacitive Touchscreen Issues Capacitive touchscreens are widely used in industrial and commercial systems due …
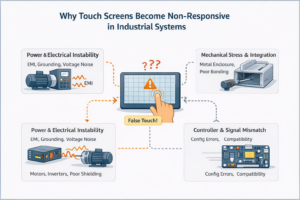
1. Understanding “Non-Responsive” Touch Screens A non-responsive touch screen refers to a condition where touch input …
Send your application details. We respond with configuration direction and next steps.